Centriols structure and functions Class 11
Автор: Bio with Maryam
Загружено: 2024-09-01
Просмотров: 81
Описание:
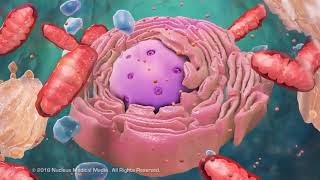
Centriols are small, cylindrical organelles found in the cells of most eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and protists. They play a crucial role in various cellular processes, including:
1. *Microtubule organization*: Centrioles act as microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs), nucleating and anchoring microtubules.
2. *Cilia and flagella formation*: Centrioles are involved in the formation of cilia and flagella, which are essential for cell movement and sensing.
3. *Cell division*: Centrioles help form the spindle fibers that separate chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis.
4. *Intracellular transport*: Centrioles assist in the movement of vesicles and organelles along microtubules.
5. *Cell signaling*: Centrioles may be involved in cell signaling pathways, although this is still being researched.
Centrioles are composed of:
1. *Microtubule triplets*: Nine microtubule triplets arranged in a cylindrical structure.
2. *Proteins*: Associated proteins, such as tubulin, tektin, and centrin, which help form and maintain the centriole structure.
There are two types of centrioles:
1. *Mother centriole*: The older, more mature centriole that gives rise to new centrioles.
2. *Daughter centriole*: The newer, less mature centriole that forms from the mother centriole.
In summary, centrioles are essential organelles that play a central role in maintaining cellular structure, function, and division!
Повторяем попытку...

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео
-
Информация по загрузке: