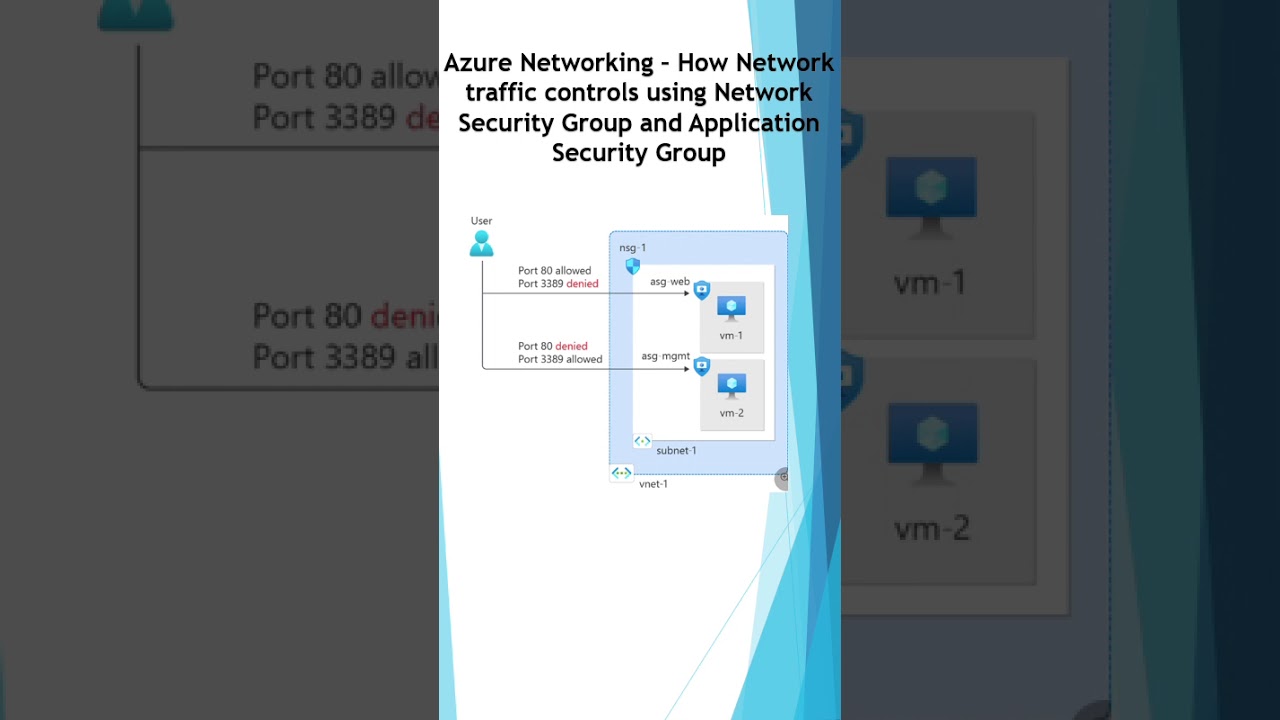
Network traffic control using NSG and ASG
Автор: Cloudence
Загружено: 2025-10-03
Просмотров: 71
Описание:
Network traffic control using NSG and ASG:
Azure Networking:
Azure Virtual Network (Vnet)
Subnet
Network Security Group - NSG
Application Security Group (ASG)
What an NSG does
Traffic Filtering: NSGs contain rules that filter inbound and outbound traffic to Azure resources.
Rule-Based Control: Rules are defined with priority, protocol (like TCP, UDP), source/destination IP addresses, and ports, allowing granular control over network flow.
Stateful Operations: NSGs are stateful, meaning that if an inbound request is allowed, the corresponding outbound response traffic is automatically authorized, and vice-versa.
How NSGs are applied
Association: NSGs can be associated with:
Subnets: To filter traffic for all resources within a virtual network subnet.
Network Interfaces (NICs): To filter traffic for a specific virtual machine.
The same NSG can be linked to multiple subnets and NICs.
Azure networking refers to Microsoft's suite of services for building, securing, and managing your network infrastructure in the cloud, with the fundamental building block being the Azure Virtual Network (VNet). A VNet provides an isolated, private network within Azure, allowing resources like virtual machines to communicate securely with each other, the internet, and your on-premises data centers. Key Azure networking services also include Azure DNS for domain name resolution, Application Gateway for web traffic management, and Azure Virtual WAN for large-scale global connectivity.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet): The primary service for creating isolated private networks in the cloud, enabling secure communication between Azure resources and external networks.
Subnets: VNets are divided into subnets, which are smaller IP address ranges used to group and isolate resources logically within the VNet.
Security Groups: Network Security Groups (NSGs) act as virtual firewalls to control inbound and outbound network traffic to and from Azure resources.
VNet Peering: A mechanism to connect two or more Azure VNets privately over the Microsoft network, allowing resources in different VNets to communicate seamlessly.
Private Link: Provides private connectivity from your VNet to Azure Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) services, keeping your traffic off the public internet.
Azure DNS: A hosted domain name system service for managing your domain names and resolving them to Azure resources.
Application Gateway & Web Application Firewall (WAF): A web traffic load balancer that also includes a Web Application Firewall (WAF) for protecting web applications from common exploits.
Azure Virtual WAN: A service that consolidates networking, security, and routing to provide end-to-end connectivity for your branches and users.
Azure Bastion: A fully managed service that provides secure and seamless RDP and SSH access to your virtual machines over TLS, directly from the Azure portal.
Network Watcher: A tool for monitoring, diagnosing, and providing insights into the health of your Azure network.
#Azure
#MicrosoftAzure
#CloudComputing
#Cloud
#Microsoft
#AzureCloud
#DevOps
#cloudservices
#AzureNetworking
#AzureNetwork
#VNet (for Virtual Networks)
#AzureVNet
#AzureDNS
#AzureFirewall
#NetworkSecurityGroups (#NSG)
#LoadBalancer (#AzureLoadBalancer)
#VPN (#AzureVPN)
#ExpressRoute
#VNetPeering
#AZ700 (for those studying for the Azure networking exam)
#AzureTutorial
#Shorts
#YouTubeShorts
#Viral
#Trending
#TechShorts
#TrendingNow
#AzureLab
#CloudTraining
#ITTraining
#TechTutorial
#AzureTips
#CloudExpert
Повторяем попытку...
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео
-
Информация по загрузке: