Cardiovascular system overview || Anatomy and physiology | Heart | Blood Flow | Bibek Gs Education
Автор: Bibek GS Education
Загружено: 2025-12-24
Просмотров: 9
Описание:
Cardiovascular system overview || Anatomy and physiology | Heart | Blood Flow | Bibek Gs Education
@bibekgseducation
.
.
.
.
The heart and cardiovascular system form a vital network that pumps blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste, with the heart acting as the central pump, and blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) as the highways, ensuring every cell gets what it needs to function. This system, controlled by the heart's electrical impulses, regulates body temperature and responds to activity, with arteries carrying blood away from the heart and veins bringing it back, all directed by four internal valves.
The Heart: The Pump
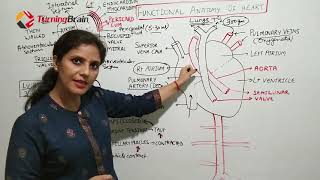
Structure: A muscular organ with four chambers (right/left atria, right/left ventricles) and four one-way valves (tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, aortic).
Function: A powerful pump, beating about 100,000 times daily, circulating about five quarts of blood per minute.
Electrical System: The sinoatrial (SA) node acts as the natural pacemaker, controlling the heartbeat's rate and rhythm.
The Blood Vessels: The Network
Arteries: Carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the body (e.g., aorta, pulmonary artery).
Veins: Carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart (e.g., vena cavae, pulmonary veins).
Capillaries: Tiny vessels connecting arteries and veins, allowing for nutrient/waste exchange at the cellular level.
How it Works (Blood Flow)
Right Side: Receives deoxygenated blood, sends it to the lungs to pick up oxygen.
Left Side: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it out via the aorta to the rest of the body.
Valves: Open and close with each beat, ensuring blood flows in only one direction, like one-way doors.
Why it's Important
Life Support: Delivers oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and infection-fighting white blood cells.
Waste Removal: Carries carbon dioxide and other waste products to be eliminated.
Regulation: Helps maintain body temperature and adapts to stress or exercise.
Common Problems
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), Heart Failure, High Blood Pressure (Hypertension), and Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats).
The cardiovascular system, also called the circulatory system, is your body's transport network, consisting of the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries), and blood, responsible for delivering oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and removing waste like carbon dioxide to keep cells healthy. The heart acts as a powerful pump, pushing blood through arteries (away from the heart) to capillaries (where exchange happens) and back via veins (to the heart) in two loops: pulmonary (to lungs) and systemic (to the body).
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart,
blood, and blood vessels. The best-known function
of the circulatory system is perhaps the transport of inhaled oxygen from the lungs to body's tissues, and removal of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction to be exhaled. Basically, oxygen-poor blood from the body returns to the right side of the heart, where it is pumped to the lungs. In the lungs, blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. Oxygen-rich blood then returns to the left side of the heart. This part of the system is called the pulmonary circuit.The left side of the heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to body's tissues, where it unloads oxygen and picks up carbon dioxide. The resulting deoxygenated blood again returns to the heart's right side to complete the cycle. This part is the systemic circuit.
The heart is enclosed in a double-walled protective sac called the pericardium. The pericardial cavity contains a fluid which serves as lubricant and allows the heart to contract and relax with minimum friction.The heart wall has 3 layers: epicardium, endocardium, and myocardium.
The contraction of the heart muscle is initiated by electrical impulses, known as action potentials. The impulses start from a small group of cells called the pacemaker cells, which constitute the cardiac
conduction system. The primary pacemaker is the
SA node, it initiates all heartbeats and controls heart rate. Apart from transporting gases, the blood also supplies body's tissues with nutrients and removes
cardiovascular system function
cardiovascular system heart diagram
heart diagram
cardiovascular system overview
cardiovascular system heart anatomy
human heart
heart function
structure of the heart
blood circulation in heart
Повторяем попытку...

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео
-
Информация по загрузке: