Parathyroid hormone (bone resorption) & Calcitonin (bone deposition)
Автор: Homework Clinic
Загружено: 2019-11-19
Просмотров: 18367
Описание:
✔ https://HomeworkClinic.com
✔ https://Videos.HomeworkClinic.com
✔ Ask questions here: https://HomeworkClinic.com/Ask
Follow us:
▶ Facebook: / homeworkclinic
▶ Review Us: https://trustpilot.com/review/homewor...
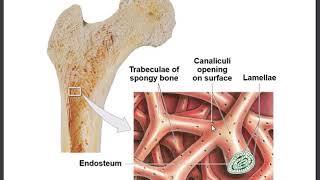
• Cellular needs for calcium may cause blood calcium concentrations to decline below the normal range.
• This decrease stimulates cells in the parathyroid gland to secrete parathyroid hormone.
• Binding of parathyroid hormone to osteoclasts in bone tissue promotes bone resorption and the release of calcium into the blood.
• As calcium enters the blood, blood calcium concentration is restored to normal levels.
Parathyroid hormone (intestinal calcium absorption, summary)
• Cellular needs for calcium may cause blood calcium concentrations to decline below the normal range.
• This decrease stimulates cells in the parathyroid gland to secrete parathyroid hormone.
• Parathyroid hormone binds to kidney cells promoting their production of calcitriol.
• Calcitriol binds with intestinal cells causing them to increase absorption of calcium.
• As calcium enters the blood, blood calcium concentration is restored to normal levels.
• Increased Parathyroid hormone secretion:
• Promotes bone resorption
• The production of calcitriol
• The result of these actions is an increase in blood calcium levels.
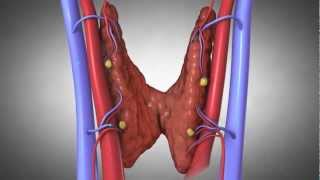
• Nutrient absorption in the small intestine may cause blood calcium concentrations to increase.
• This rise stimulates parafollicular cells in the thyroid gland to secrete calcitonin.
• Calcitonin interacts with osteoblasts in bone tissue and stimulates them to take up calcium from the blood and deposit it in the bone matrix.
• This lowers the blood calcium concentration to normal.
Повторяем попытку...

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео
-
Информация по загрузке: