154 Control flow and control structure
Автор: Engineering Academy Online
Загружено: 2024-11-15
Просмотров: 7
Описание:
Certainly! Here's a small description of *Control Flow* and *Control Structures* in Python:
*Control Flow and Control Structures in Python*
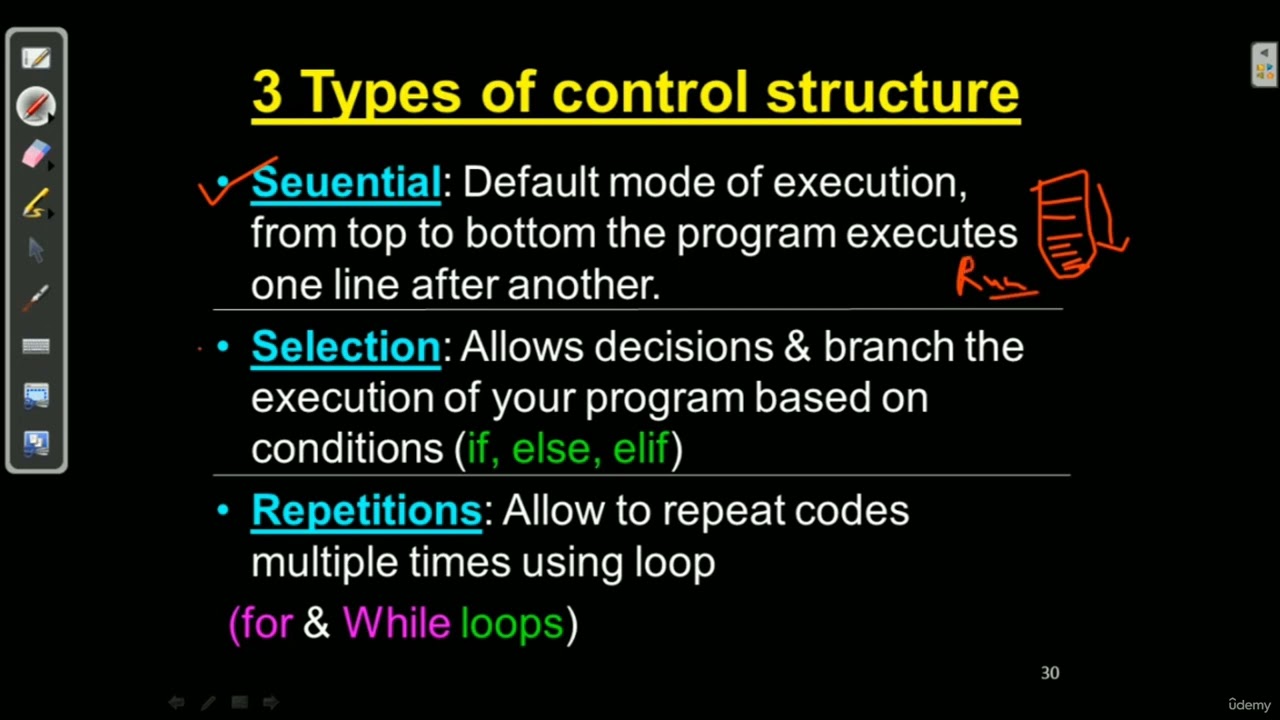
*Control flow* refers to the order in which individual statements, instructions, or function calls are executed or evaluated in a program. In Python, *control structures* are used to control the flow of execution based on certain conditions, allowing you to make decisions, repeat operations, and alter the flow of execution.
Python provides several types of control structures:
1. **Conditional Statements (if, elif, else)**:
Used to make decisions in your code. Based on the evaluation of a condition (which returns `True` or `False`), different blocks of code can be executed.
**if**: Executes a block of code if the condition is `True`.
**elif**: Checks an additional condition if the `if` condition is `False`.
**else**: Executes a block of code when all preceding conditions are `False`.
Example:
```python
x = 10
if x 0:
print("Positive number")
elif x 0:
print("Negative number")
else:
print("Zero")
```
2. **Loops (for and while)**:
Used to repeat a block of code multiple times.
**for loop**: Iterates over a sequence (like a list, tuple, or range) and executes a block of code for each item.
**while loop**: Repeats a block of code as long as a given condition is `True`.
Example:
```python
for loop
for i in range(5):
print(i)
while loop
count = 0
while count 5:
print(count)
count += 1
```
3. **Break and Continue**:
**break**: Exits the loop entirely, regardless of the loop condition.
**continue**: Skips the current iteration and continues with the next iteration of the loop.
Example:
```python
break example
for i in range(10):
if i == 5:
break
print(i)
continue example
for i in range(5):
if i == 3:
continue
print(i)
```
4. **Pass**:
*pass* is a placeholder statement used when no action is needed. It allows the program to continue without doing anything.
Example:
```python
if x 10:
pass # Do nothing if x is greater than 10
```
**Why Control Structures Matter**:
Control structures enable *dynamic behavior* in your programs. They help you make decisions (using `if` statements), repeat actions (using loops), and respond to changing conditions (using `break`, `continue`, or `pass`), making your code more powerful and flexible.
Would you like examples or further explanations of any specific control structure?
Повторяем попытку...
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео
-
Информация по загрузке: