Mirror
Автор: Physics with Momin khan
Загружено: 2025-06-20
Просмотров: 19
Описание:
A mirror is a smooth, highly polished surface that reflects light in a regular and predictable manner, allowing for the formation of images. Unlike rough surfaces that scatter light, mirrors are designed to reflect almost all incident light, obeying the law of reflection, which states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
Historically, the earliest "mirrors" were simply calm pools of water or polished stones like obsidian, dating back as far as 4000 BCE. Later, people crafted mirrors from polished metals such as bronze, silver, and gold. The invention of glass mirrors, coated with a reflective metal (traditionally silver or aluminum), revolutionized their clarity and widespread use.
How Mirrors Work
When light rays from an object strike a mirror's smooth surface, they bounce back. Your eyes then perceive these reflected rays as an image. The smoothness of the mirror's surface is crucial because it ensures that light rays reflect uniformly, maintaining the coherence needed to form a clear image.
Types of Mirrors
Mirrors are primarily categorized based on the shape of their reflective surface:
Plane Mirrors:
Description: These are the most common type, featuring a flat, perfectly smooth reflective surface.
Image Formation: Plane mirrors produce images that are:
Virtual: The light rays do not actually converge at the image location; rather, they appear to originate from behind the mirror.
Upright (Erect): The image is not inverted.
Same size: The image is the same size as the object.
Laterally inverted: The image is reversed from left to right (e.g., your right hand appears as the left hand of your reflection).
Same distance: The image appears to be the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front.
Uses: Widely used in homes for personal grooming (bathroom mirrors, dressing tables), in shops, and for decorative purposes to create an illusion of space.
Spherical Mirrors:
Spherical mirrors are sections of a sphere whose reflecting surface is curved. They are further divided into two main types:
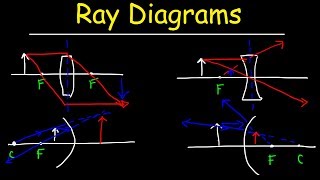
a. Concave Mirrors (Converging Mirrors):
Description: These mirrors are curved inward, like the inside of a spoon or a bowl. Their reflective surface is on the inner side of the sphere.
Image Formation: The type and characteristics of the image formed by a concave mirror depend on the object's position relative to the mirror's focal point and center of curvature:
Can form both real (where light rays actually converge) and virtual images.
Can form inverted or upright images.
Can form images that are magnified, diminished, or same size as the object.
When an object is placed very close to a concave mirror (within its focal length), it produces a magnified, virtual, and upright image.
Uses:
Shaving and makeup mirrors: To produce a magnified view of the face.
Dentist's mirrors: For magnified views of teeth.
Car headlights and searchlights: To produce a strong, parallel beam of light by placing the bulb at the focal point.
Reflecting telescopes: To gather and focus light from distant objects.
Solar furnaces: To concentrate sunlight to generate heat.
b. Convex Mirrors (Diverging Mirrors):
Description: These mirrors are curved outward, like the back of a spoon. Their reflective surface is on the outer side of the sphere.
Image Formation: Convex mirrors always produce images that are:
Virtual: The light rays diverge after reflection and appear to originate from behind the mirror.
Upright (Erect): The image is never inverted.
Diminished (Smaller): The image is always smaller than the actual object.
Uses:
Rear-view mirrors in vehicles: To provide a wider field of view, albeit with smaller images, enhancing safety.
Shop security mirrors: To monitor a large area.
Street light reflectors: To spread light over a wider area.
Blind spots at intersections: To help drivers see around corners.
In summary, mirrors are fundamental optical devices that utilize the principle of reflection to form images. Their diverse shapes and properties allow for a wide range of applications, from everyday grooming to advanced scientific instruments.
Повторяем попытку...

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео
-
Информация по загрузке: