Photosynthesis Meaning
Автор: GENETIC TEACHER
Загружено: 2024-09-01
Просмотров: 103
Описание:
#Photosynthesis_Meaning
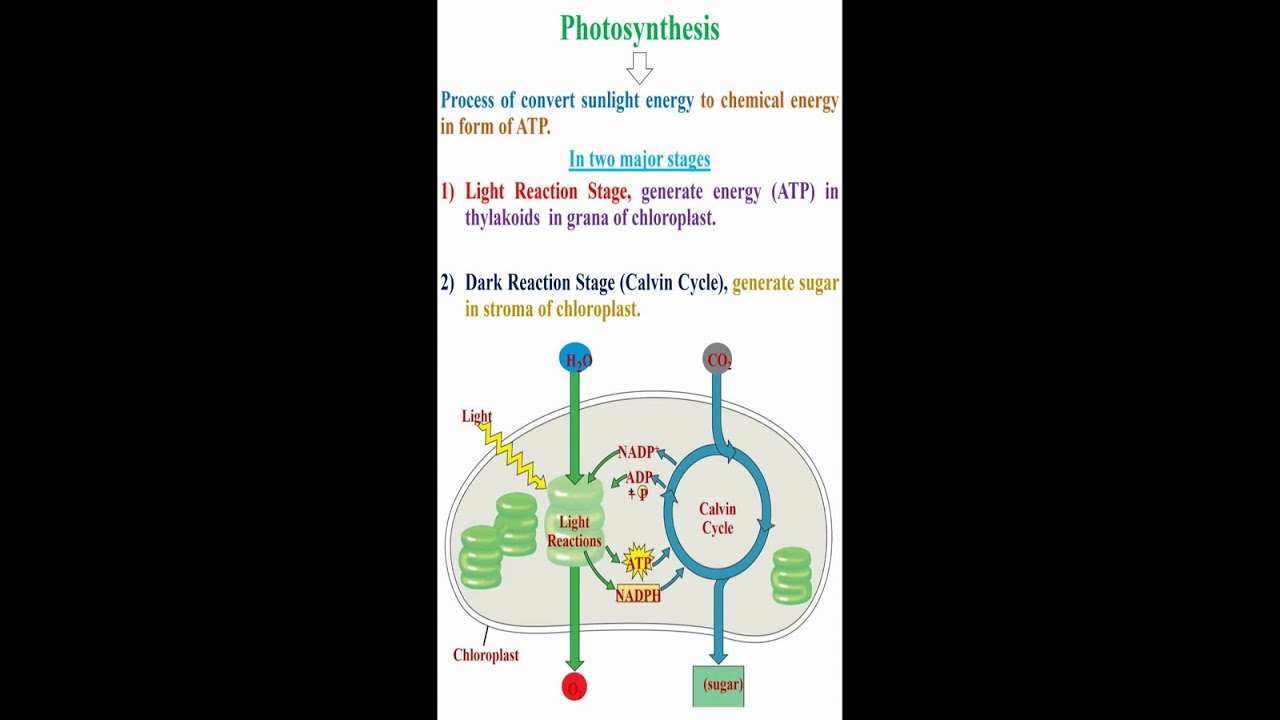
Photosynthesis, Process of convert sunlight energy to chemical energy in form of ATP, two major stages, Light Reaction Stage, generate energy (ATP) in thylakoids in grana of chloroplast, Dark Reaction Stage (Calvin Cycle), generate sugar in stroma of chloroplast, Photosynthesis Stage, Photolysis, Carbon Fixation, Grana, Stroma, chloroplast, Requires Light, Requires Chlorophyll, Raw Material, Water (from soil via plant roots), Carbon Dioxide (from air via stomata), Products, Hydrogen, Oxygen, ATP, Glucose, metabolic activity, ribosome, mitochondria, nucleus, nitrogen, protein, starch, nitrates, amino acids, protein for growth and repair, sucrose in fruits, fats and oil for storage and cell membrane, starch for storage, cellulose for cell wall, nucleic acids for DNA and genetic materials, respiration for energy release, Photosynthesis Limited Factors, Light Intensity, split Water into Hydrogen and Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide Concentration, make Glucose, Temperature, Enzymes work too slowly at low temperatures, and denature at too high temperatures, If photosynthesis decreases, cell growth decreases, Plastid Types, Chromoplasts, color plastids found in all flowers and fruits, and responsible for their distinctive colors, Chloroplasts, green colored plastids within plant cell chlorophyll, Leucoplasts, colorless plastids use for storage starch, lipids, and proteins within plant cell, Chloroplast, Found in all green plants and algae in guard cells in leaves and within mesophyll of plant cell, Synthesize food by process of photosynthesis by absorbs sunlight energy and converts it into chemical energy in form of ATP by releasing oxygen from water, Plant food producers, Carbon Dioxide (CO2) obtain from air use to generate carbon and sugar during Calvin Cycle or dark reaction of photosynthesis, Some glucose converted to starch for storage, Some glucose converted to cellulose to build cell wall, Chlorophyll, green photosynthetic pigment help in process of photosynthesis, Grana, Made up of disc-shaped (10-20 Thylakoids), Consists of chlorophyll pigments, so it consider functional unit or site of conversion of light energy into chemical energy, Stroma, Homogenous matrix contains grana in similar to cytoplasm in cells, Contains various enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and others, Cellular Respiration, Cells obtain energy from sugar, Break down sugar to release energy, anaerobic respiration, absence of oxygen, aerobic respiration, present oxygen, alcohol fermentation, lactate fermentation, glycolysis cycle, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain cycle, Photosynthesis, Produce food, Store energy , Occur in cells containing chloroplasts, Release oxygen, Use water, Use carbon dioxide, Use sunlight, Respiration, Use food for energy, Release energy, Occur in all cells, Use oxygen, Produce water, Produce carbon dioxide, Use light and dark, ATP, ADP, High energy molecule, low energy molecule, Transpiration, Water Evaporation, Loss water vapor from leaf via stomata, Plant transpires 90% water that enter through roots, 10% water use in chemical processes in plant tissues, Stomata, Pores found on plant leaves and stems, Used to control gas exchange (O2 and CO2), Guard Cells, Surround each stoma, To regulate transpiration rate, By opening and closing stomata, Water Functions, Transport minerals through plant, Cool plant, Move sugars and plant chemicals, Maintain turgor pressure, When plants don't have enough water, turgor pressure lost and plant starts to wilt, Nitrogen, Growth Stems and Leaves, Phosphorus, Healthy Roots, Potassium, Healthy Leaves and Flowers, Calcium, Healthy Growth of New Stems, Magnesium, Making Chlorophyll, Monocots, have one seed leaf (cotyledon), Dicots, have two seed leaves (2 cotyledon), Simple Leaf, Compound Leaf, Doubly Compound Leaf, Stems Types, Herbaceous Stems, Woody Stems, Provide support, Transport water through xylem, Transport nutrients through phloem, Taproots, absorb water deep in ground such as carrots, Fibrous roots, stay close to top soil such as tomato, Adventitious roots, helps plant climb such as strawberries, Primary roots, first growth roots, Secondary roots, branches of primary roots, Root hairs, responsible for water movement to leaves, Stamen, Pistil, Anther, Stigma
#geneticteacher
Free online Lectures and Notes in Biological Sciences, Life Sciences, Biotechnology, Biosciences, Bioinformatics, Genetic, Cytogenetic, Genetic Engineering, Germplasm Resources, Biodiversity, Biostatistics, Biochemistry, Microbiology, Agriculture Sciences, Botany, Zoology, Animal Sciences, Environmental Sciences, Plant Sciences, Plant Breeding, Crop Sciences, Horticultural Sciences, Molecular Genetics, Molecular Markers, Genetic Diversity, Plant Tissue Culture, Microbial Genetics, Quantitative Genetic, Genomic, Immunology, Mutations and Population Genetics.
Subscribe #geneticteacher in YouTube / @geneticteacher
Повторяем попытку...
Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео
-
Информация по загрузке: