Solid Angle
Автор: Learning Hub
Загружено: 2023-06-22
Просмотров: 106
Описание:
In geometry, a solid angle is a measure of the amount of space or solid content spanned by a three-dimensional angle. It is analogous to the concept of a two-dimensional angle, which measures the amount of rotation in a plane. While a two-dimensional angle is measured in radians or degrees, a solid angle is measured in steradians (sr).
To visualize a solid angle, imagine a point source of light radiating in all directions. The solid angle represents the portion of the surface of an imaginary sphere that is enclosed by a cone emanating from the point source. The apex of the cone is at the point source, and the base of the cone is defined by the surface area that intersects the sphere. The solid angle is the ratio of the area of the base of the cone to the square of the radius of the sphere.
Mathematically, the formula for calculating the solid angle Ω in steradians is:
Ω = A / r²
where A is the area of the base of the cone and r is the radius of the sphere. The unit of measurement, steradian, is derived from the words "steres" (solid) and "radian" (angular measure).
Solid angles are used in various fields of physics and engineering, particularly in areas related to radiation, optics, and electromagnetic theory. They are also useful in describing the coverage or divergence of light sources, the measurement of radiant intensity, and calculations involving spherical symmetry.
Повторяем попытку...

Доступные форматы для скачивания:
Скачать видео
-
Информация по загрузке:




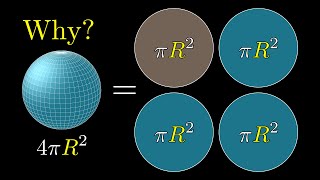













![Как сжимаются изображения? [46 МБ ↘↘ 4,07 МБ] JPEG в деталях](https://ricktube.ru/thumbnail/Kv1Hiv3ox8I/mqdefault.jpg)
