Technologies Discussion

ЭМС № 73. EN 61000-4-11: Провалы, колебания и прерывания переменного напряжения. Зачем проводить ...

Децибел № 2. Преобразование децибел: от отношения к дБ/дБм и обратно с наглядными примерами для т...

АЦП № 1. Как преобразовать аналоговые данные в цифровые. 3 процесса АЦП: выборка, квантование, ко...

Цифровой трансивер № 1. Компонент цифрового трансивера: кодер источника, шифрование, кодер канала.

Отношение сигнал/шум № 3. Определение коэффициента шума и коэффициента шума: факторы, ухудшающие ...

Децибел № 1. Не путайте децибелы и ватты! Почему мы используем дБ и дБм для расчёта мощности и ус...

Антенна № 22. Визуализация поведения муравья: 3D-диаграмма направленности, 2D-полярная и 2D-декар...

ИИ № 4. Как 5 основных компонентов ИИ (пример) создают автономные транспортные средства (будущее ...

ИИ № 3. Как ИИ «видит» (воспринимает) изображения и «понимает» ваш язык (объяснение мультимодальн...

AI #2. Reasoning Vs Problem-Solving: Most of the Time, Reasoning First Before Problem-Solving.

AI #1. AI Components: Learning, Reasoning, Problem-solving, Perception, Language Understanding.

EMC #28. Shielding Design: Near Field, Low Freq (E- & H-field) & Far Field, High Freq (Plane Wave)

EMC #21. Absorption or Reflection? How to Properly Design a Shield Against ALL EMI Fields.

How 5G, Edge Computing & Portable Cloud Making Supercomputing Power Cheap & Accessible for Everyone.

Satellite Communication #5. Apogee & Perigee, Ascend & Descend Nodes, Line of Apsides & Eccentricity

S-Parameters #10. VNA Measurement: How to Shift Reference Planes for S-Parameter Data & De-embedding

Antenna #21. How to Derive Free Space Path Loss (FSPL) Equation from Friis Transmission Formula

Radio Wave Propagation #2. How to Obtain Max Distance of Space Wave Direct & Ground Reflected Waves.

Transmission Line #1. Circuit Theory (Low Freq) Vs Tx Line Theory (High Freq) Becos λ Circuit Size.

Power Divider #5. The 3dB Loss Mystery - Why T-Junction Resistive Dividers Waste Half Your Power.
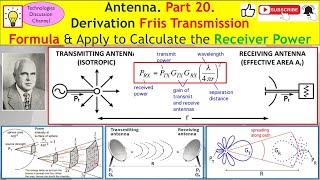
Antenna #20. How to Derive the Friis Transmission Equation & Apply to Calculate Receiver Power, Pr.

Microwave #2. Gauss, Faraday & Ampère: The Maxwell's Laws That Make Wireless Communication Work.

ZigBee #1. How This Global Standard Power Smart Applications with Low Cost, Long Battery Life & More

Multiple Access #2. Network Sharing: Multiplexing Vs Multiple Access Methods. Sharing Resources.

Multiple Access #1. Transmission Modes Made Simple: A Guide to Simplex, Half Duplex & Full Duplex.

S-Parameters #5. Is Your Network Reciprocal & Lossless? How to Find the Input Return Loss Explained.

S-Parameters #4. Reason RF Design Uses Power Waves Instead of Voltage & Current for S-Parameters.

Impedance Matching #3. How to Design 2 Two Elements L-Section Guide. Series & Shunt (Ind/ Cap)
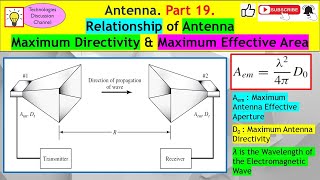
Antenna #19. How to Proof the Max Directivity & Effective Area Relationship (Derivation + Equation)

Impedance Matching #1. How to Design a Match Transformer for Max Pwr Transfer to Eliminate Mismatch.